34
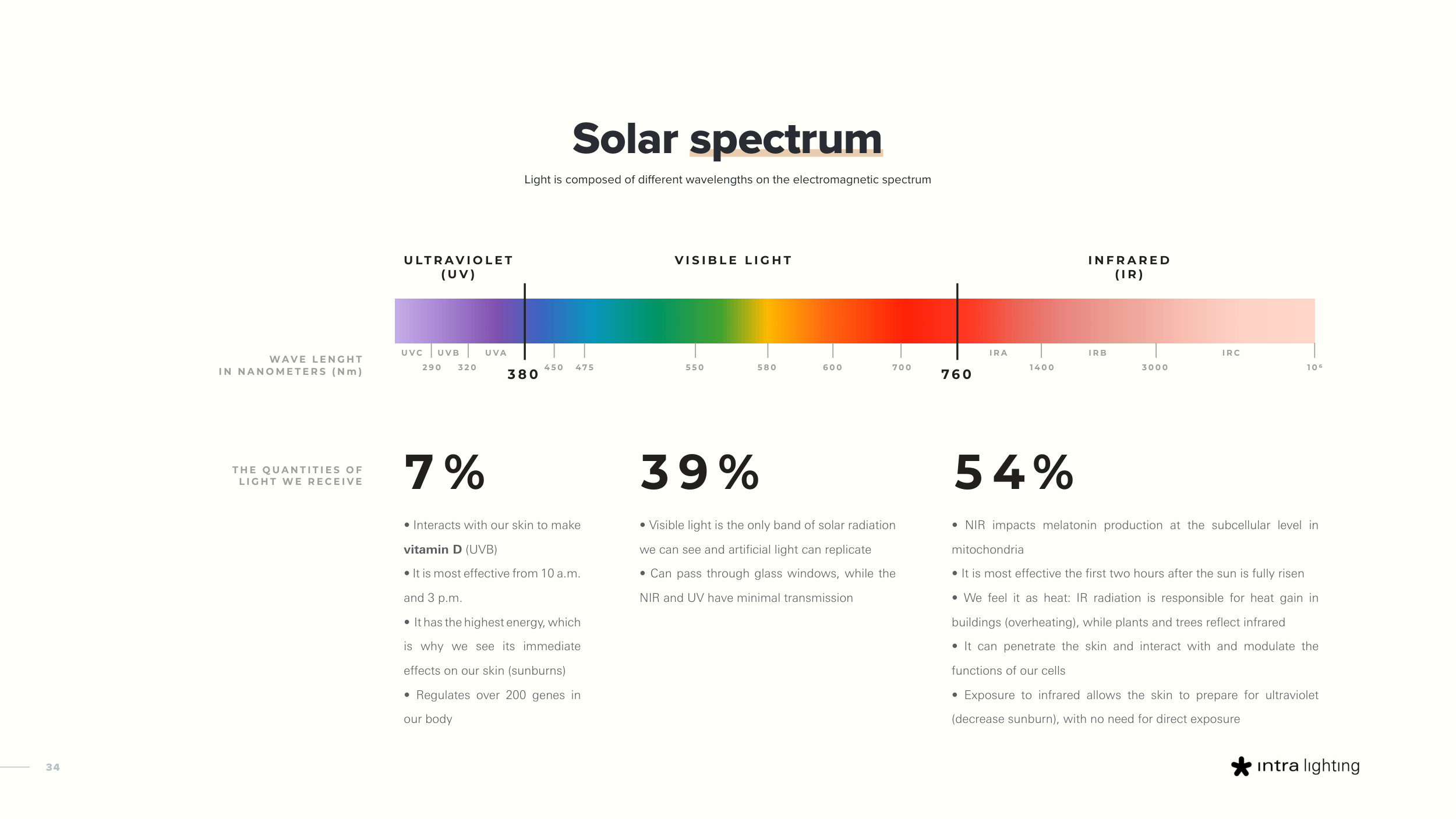
Solar spectrum
2 9 0
1 4 0 0
I R A
U V A
U V B
U V C
I R B
I R C
3 0 0 0
1 0 6
3 2 0
4 5 0
3 8 0
7 %
3 9 %
5 4 %
7 6 0
U LT R A V I O L E T
( U V )
W A V E L E N G H T
I N N A N O M E T E R S ( N m )
T H E Q U A N T I T I E S O F
L I G H T W E R E C E I V E
I N F R A R E D
( I R )
V I S I B L E L I G H T
4 7 5
5 5 0
5 8 0
6 0 0
7 0 0
• Interacts with our skin to make
vitamin D (UVB)
• It is most effective from 10 a.m.
and 3 p.m.
• It has the highest energy, which
is why we see its immediate
effects on our skin (sunburns)
• Regulates over 200 genes in
our body
• Visible light is the only band of solar radiation
we can see and artificial light can replicate
• Can pass through glass windows, while the
NIR and UV have minimal transmission
• NIR impacts melatonin production at the subcellular level in
mitochondria
• It is most effective the first two hours after the sun is fully risen
• We feel it as heat: IR radiation is responsible for heat gain in
buildings (overheating), while plants and trees reflect infrared
• It can penetrate the skin and interact with and modulate the
functions of our cells
• Exposure to infrared allows the skin to prepare for ultraviolet
(decrease sunburn), with no need for direct exposure
Light is composed of different wavelengths on the electromagnetic spectrum
L I G H T & W E L L - B E I N G
01
02
03
04