WWW.BEL-LIGHTING.COM
198
Kleurtemperatuur
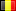
De kleurtemperatuur van een lichtbron word gedefinieerd ten opzichte van een “zwarte straal“ en weergegeven op de “Planck curve“,
zoals weergegeven op het diagram. Hoe meer de kleurtemperatuur van deze “ zwarte straal” hoog is, hoe hoger het blauw spectrum
is en hoe minder rood aanwezig is.
Θερμοκρασία χρώματος
Η θερμοκρασία χρώματος της φωτεινής πηγής ορίζεται σε σχέση με ένα «μαύρο σώμα καλοριφέρ» και αποτυπώνονται σε αυτό που
είναι γνωστό ως η «καμπύλη ακτινοβολητή Planck», όπως φαίνεται στο διάγραμμα. Όσο υψηλότερη είναι η θερμοκρασία αυτής της
«μαύρης καλοριφέρ σώμα» είναι υψηλή, τόσο μεγαλύτερη είναι η μπλε συνιστώσα του φάσματος και η μικρότερη είναι η κόκκινη
συνιστώσα.
La température de couleur d’une source lumineuse est définie par rapport à un «corps radiateur noir» et reportée sur ce qui est connu
sous le nom de la «courbe de Planck», comme le montre le diagramme. Plus la température de ce «corps radiateur noir» est élevée,
plus grande est la composante bleue du spectre et plus petite la composante rouge.
La température de couleur
The color temperature of a light source is defined in relation to a «black body radiator» and plotted on what is known as the «Planckian
curve» as shown in the diagram. The higher the temperature of this «black body radiator», the greater the blue component of the
spectrum and the smaller the red component.
Color temperature
Die Farbtemperatur einer Lichtquelle wird anhand eines „schwarzen Strahlkörpers“ definiert und auf die „Plancksche Kurve“
übertragen, wie in dem Diagramm dargestellt. Je höher die Temperatur des „schwarzen Strahlkörpers“, desto höher ist der Blauanteil
des Spektrums und desto kleiner ist der Rotanteil.
Farbtemperatur
Indicative:
Luminance
Chromacity Diagram
Color temperature
candle
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
sunrise - sunset
morning -
afternoon
midday
medium
light
great sun
overcast haze
warm white
< 3500 K°
neutral white
> 3500 K°
daylight
> 5000 K°