PERFORMANCE iN LIGHTING | powered by GEWISS
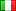
SR
075
100
125
150
HUGE
WIDE
ST1
CYCLE
H
L
Two-way traffic
One-way traffic
Road optics
Optics for pedestrian crossings
Road optics are identified as the optics that have a very broad beam spread
on the β plane (usually greater than 120°), with the point of maximum
emission on one of the adjacent planes to the latter, up to a maximum of 45°.
Road lighting based on L/H ratio that can be found in road lighting systems,
where:
- L: distance between the optical axes of the luminaire and the part of the
area furthest from it with its own requirements.
- H: height of installation of the luminaire.
Example
Acronym of the road optics based on the L/H ratio: R/xxx
where:
R = road
xxx = L/H value (e.g. 100 = 1.00)
For example: R/075, R/100
For optics for pedestrian crossings are identified those optics for lighting in
the direction of their flow.
They feature asymmetrical emission both on the α plane and on the β plane.
Example
Acronym of optics for pedestrian crossings: Z/R
where:
Z = zebra (pedestrian crossing)
R = right (for countries where driving is on the right)
Name of the road optics based on the L/H ratio:
Type of optic
Acronyms
Description
Optic for L/H up to 0.75 (0,5 ≤ L/H ≤ 0,875)
Optic for L/H of 1 (0,875 ≤ L/H ≤ 1,125)
Optic for L/H of 1.25 (1,125 ≤ L/H ≤ 1,375)
Optic for L/H of 1.5 (1,375 ≤ L/H ≤ 1,625)
Identifying and classifying our optics
Mandatory
indications
Additional
indications
Acronyms
Description
Optics for wide road geometries
Optics for medium road geometries
Optics for medium-wide road geometries
Optics for pedestrian crossings
XXVI