L&L Luce&Light
904
PRI
SEC
CONST
CONSTANT
CURRENT
350mA
+
-
+
+
-
-
L
N
PRI
SEC
24Vdc
+
-
L
N
+
+
+
+
-
-
-
-
CONSTANT
VOLTAGE
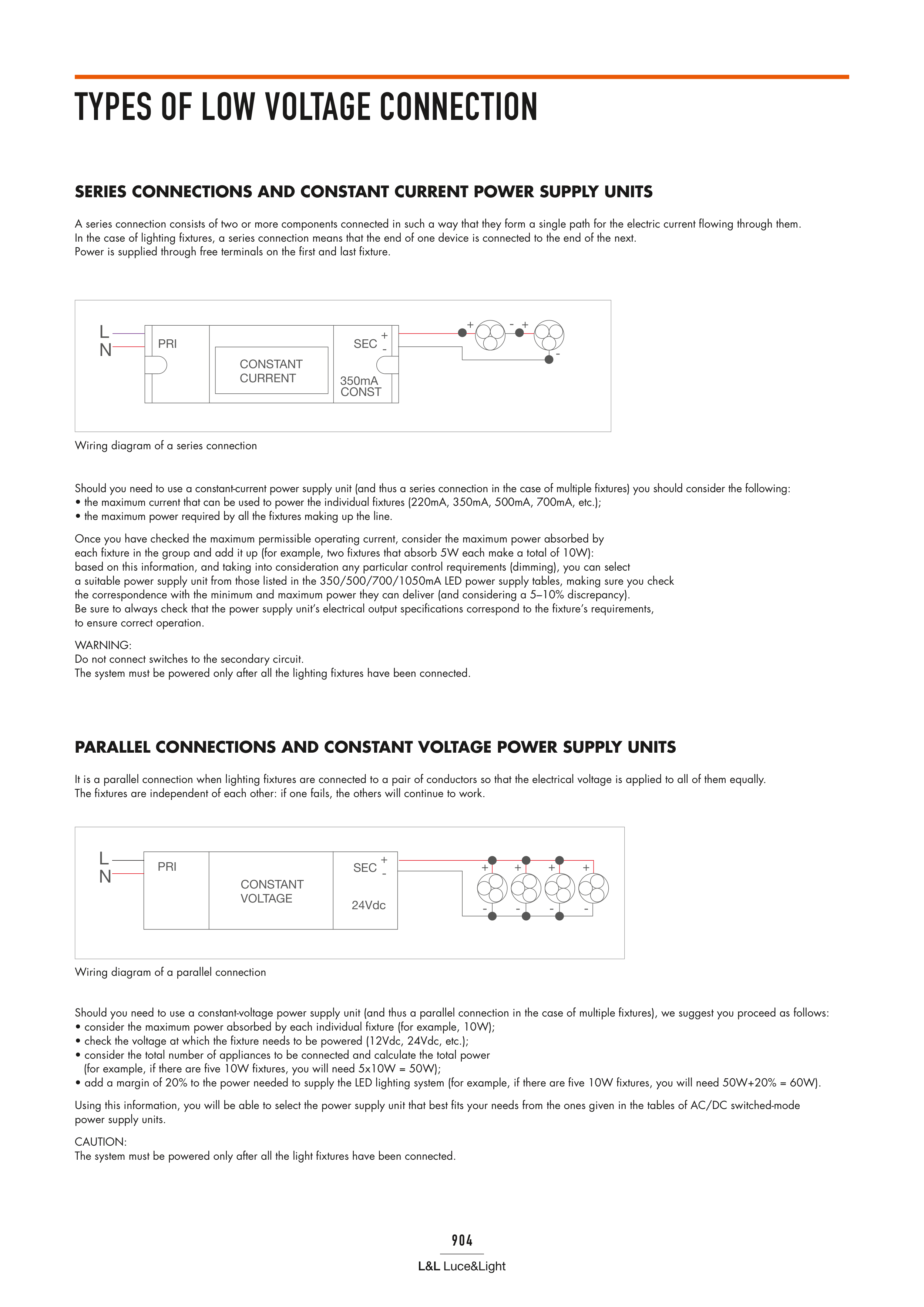
Wiring diagram of a series connection
Wiring diagram of a parallel connection
SERIES CONNECTIONS AND CONSTANT CURRENT POWER SUPPLY UNITS
A series connection consists of two or more components connected in such a way that they form a single path for the electric current flowing through them.
In the case of lighting fixtures, a series connection means that the end of one device is connected to the end of the next.
Power is supplied through free terminals on the first and last fixture.
It is a parallel connection when lighting fixtures are connected to a pair of conductors so that the electrical voltage is applied to all of them equally.
The fixtures are independent of each other: if one fails, the others will continue to work.
Should you need to use a constant-current power supply unit (and thus a series connection in the case of multiple fixtures) you should consider the following:
• the maximum current that can be used to power the individual fixtures (220mA, 350mA, 500mA, 700mA, etc.);
• the maximum power required by all the fixtures making up the line.
Once you have checked the maximum permissible operating current, consider the maximum power absorbed by
each fixture in the group and add it up (for example, two fixtures that absorb 5W each make a total of 10W):
based on this information, and taking into consideration any particular control requirements (dimming), you can select
a suitable power supply unit from those listed in the 350/500/700/1050mA LED power supply tables, making sure you check
the correspondence with the minimum and maximum power they can deliver (and considering a 5–10% discrepancy).
Be sure to always check that the power supply unit’s electrical output specifications correspond to the fixture’s requirements,
to ensure correct operation.
WARNING:
Do not connect switches to the secondary circuit.
The system must be powered only after all the lighting fixtures have been connected.
PARALLEL CONNECTIONS AND CONSTANT VOLTAGE POWER SUPPLY UNITS
Should you need to use a constant-voltage power supply unit (and thus a parallel connection in the case of multiple fixtures), we suggest you proceed as follows:
• consider the maximum power absorbed by each individual fixture (for example, 10W);
• check the voltage at which the fixture needs to be powered (12Vdc, 24Vdc, etc.);
• consider the total number of appliances to be connected and calculate the total power
(for example, if there are five 10W fixtures, you will need 5x10W = 50W);
• add a margin of 20% to the power needed to supply the LED lighting system (for example, if there are five 10W fixtures, you will need 50W+20% = 60W).
Using this information, you will be able to select the power supply unit that best fits your needs from the ones given in the tables of AC/DC switched-mode
power supply units.
CAUTION:
The system must be powered only after all the light fixtures have been connected.
TYPES OF LOW VOLTAGE CONNECTION